Study Sheet for Test 3
Chapter 6—The Politics of Public Opinion
6.1 The Nature of Public Opinion
What is Public Opinion
Political Socialization
Polarization
Socialization Agents
Diffuse Support
Family
Schools
Peers
Religion
Media
Overt v. Covert
Socialization and Ideology
The Ideological Spectrum
Communist
Socialist
Liberal
Center
Conservative
Authoritarian
Fascist

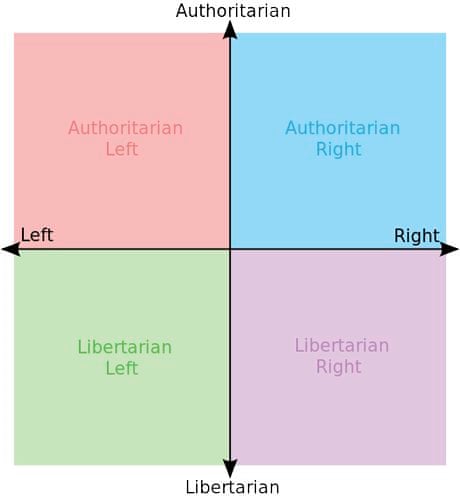
Possibly better political compass (see image above)
6.2 How is Public Opinion Measured?
Taking a Poll
Straw Polls
Scientific Polls
**universe v. sample**
**size of sample, known as the "n"**
**weighting of poll data**
Random Sample
Representative Sample
Margin of error
Technology of Polling
Face-to-Face
Phone
Issues with phone polling
"Robo-polls" vs. actual humans
Shift to cell phones
Internet polls
Are they ever accurate?
Problems in Polling
Framing of a question
Leading questions
The Bradley Effect
Push Polls
6.3 What does the Public Think?
Experiences that Affect Public Opinion
Heuristics
Demographic Influence on Voting
Political Cultures
Political Elites
Opinions About Politics and Policies
This section has a lot of extraneous filler--don't worry about it
Public Opinion and Political Institutions
The Presidency
Congress
The Supreme Court
6.4 The Effects of Public Opinion
Delegate vs. **Trustee**
Theory of delegate representation
Public Opinion and Elections
Favorability Polls
Bandwagon Effect
Horserace Coverage
Public Opinion and Government
Need for politicians and policy makers to keep abreast of public opinion
Power of a popular president
The House and public opinion
The Senate and public opinion
The Supreme Court and public opinion
Chapter 7—Voting and Elections
7.1 Voter Registration
The 24th Amendment
The Voting Rights Act of 1965
Shelby County v. Holder (2013)
How Does someone Register to Vote?
Residency Requirement
Registration
Motor Voter Law (1993)
Help America Vote Act (2002)
Who is Allowed to Register?
Age, Citizenship, Resident
Mentally competent?
In Jail?
7.2 Voter Turnout
Counting voters
Total Population
Voting Age Population (VAP)
Voting Eligible Population (VEP)
Total Registered Voters
What Factors Drive Turnout?
Targeting of Likely Voters
Age
Socioeconomic Status (SES)
Race
Gender
What Factors Decrease Turnout?
Not Mandated
Voter ID Laws
Lack of Early Voting
Apathy
Voter Fatigue
7.3 Elections
Deciding to Run
Types of people who run
Female participation
Incumbent
War Chest
Campaign Finance Law
**Hard Money v. Soft Money**
**Tillman Act**
Rise of Political Action Committees (PACs)
Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) of 1971
Individual Limits on Giving ($2700 x 2)
Creation of the Federal Election Commission (1974)
Buckley v. Valeo (1976)
Bipartisan Campaign Finance Reform Act of 2002 (McCain-Feingold)
Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission (2010)
Rise of Super-PACs
Important: know the difference between a PAC and a Super PAC
Nomination Stage
Closed Primary
Open Primary
Jungle (Top-Two) Primary
Caucus (and whether they are A Bad Thing)
Primary (and the controversy over the dates of presidential primaries)
Delegates
Convention Season
No surprises
**Brokered Convention**
Planks
Platform
General Elections and Election Day
Debates
The Electoral College
**Traditional System--electors chosen to exercise discretion with two votes, both for president**
**End of this system due to parties and the crazy election of 1800**
**Passage of the 12th Amendment, rise of Presidential Tickets**
Faithless Electors
Winner-Take-All (except for Maine and Nebraska)
Midterm Elections
No coattail effect
7.4 Campaigns and Voting
Fundraising
Dialing for Dollars
Primary v. General Elections
Primaries are harder for voters
Importance of Name recognition
Political Ads
"Shadow Campaigns"
Technology
Rise of Radio (FDR)
Television (JFK)
"Strand By Your Ad" Provision
Websites
**Social Media and Donald Trump**
Voter Decision Making
Party Affiliation
Straight-Ticket Voting
**Split-Ticket Voting**
Ballot fatigue
Retrospective Voting
Pocketbook Voting
Prospective Voting
Incumbency Advantage
Franking
Gerrymandering
7.5 Direct Democracy
Direct Democracy Defined
Referendum
Initiative
Recall
Policymaking Through Direct Democracy
Chapter 8—The Media
8.1 What is the Media?
Media Basics
Mass Media
Public Relations
Media Types
Television
Cable/Satellite
Online News
Conglomerate Control
**But how many people still get their news from broadcast today?**
Functions of the Media
Agenda Setting
**Gatekeeping and its decline with the proliferation of new media**
8.2 Evolution of the Media
Print Media
Party Press Era
Yellow Journalism
The Informational Model
Muckraking
Financial Weakness Today
Paywalls
Radio
FDR and his Fireside Chats
Communications Act of 1934
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Television
Power of the medium
New Media Trends
Rise of the Internet
Youtube
Citizen Journalism
"Infotainment"
**Social Media, Twitter, Polarization and Trump**
8.3 Regulating the Media
Media and the First Amendment
The Zenger Case (1735)
Slander and Libel
You should already know this from the last test!
Classified Material
You should already know this from the last test!
Media and FCC Regulations
Equal-Time Rule
Death of the Fairness Doctrine
Indecency Regulations
Telecommunications Act of 1996
Media and Transparency
Sunshine Laws
Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) of 1966
Journalists in War
"Reporter's Privilege"
Branzburg v. Hayes (1972)
**Shield Laws**
8.4 Impact of the Media
Media Effects and Bias
Hypodermic Theory
Minimal Effects Theory
Cultivation Theory
Framing
Episodic v. Thematic
Coverage Effects on Governance and Campaigns
Less Air Time for Public Officials
Bypassing the Media (Donald Trump)
Relationship with the Press
Chapter 9—Political Parties
9.1 What are Parties and How Did They Form?
Political Parties as Unique Organizations
Difference Between Parties and Interest Groups
Party Platform
How Parties Formed
Federalists v. Democratic-Republicans
Democrats v. Whigs
Republicans v. Democrats
Third Parties
9.2 The Two-Party System
Election Rules and the Two-Party System
**Duverger's Law**
Plurality Voting--"First Past the Post"
Proportional Representation and Multiparty States
Majoritarian Voting
NOTE: We have neither PR nor Majoritarian elections in general elections in the USA!
**Third Parties Sting and Die**
Critical Elections and Realignment
9.3 The Shape of Modern Political Parties
The Party-in-the-Electorate
Party Identifiers
Identification v. Membership
Party Organization
Local Organization
Precinct
County
State Organizations
National Party Organization
Political Conventions
Decline in importance and media coverage
The Party-in-Government
Need to achieve policy goals
Party Conferences/Caucuses
Role of Whips
Separation of Powers as an Impediment
Majority Party
Minority Party
9.4 Divided Government and Political Parties
The Problem of Divided Government
**Is it necessarily a problem?**
Bipartisanship
Implications of Polarization
Dissimilarity between Democrats and Republicans
Rise of the Tea Party
Occupy Wall Street, Black Lives Matter
Fewer Laws Passed
Government Shutdowns
Causes of Polarization
Sorting
Gerrymandering
Reapportionment
Redistricting
Safe Seats
**Geographic movement**
**Collapse of the Manufacturing Sector**
**Rise of the Meritocratic Elite**
NOTE: Double asterisks indicate items not covered in the text that I still want you to know.